40. Finance Coursework Help

Progressive writing skills offers expert financial services, including M&A, financial modeling, corporate finance, and behavioral finance, with competitive pricing, discounts, and no hidden fees.

Progressive writing skills offers expert financial services, including M&A, financial modeling, corporate finance, and behavioral finance, with competitive pricing, discounts, and no hidden fees.
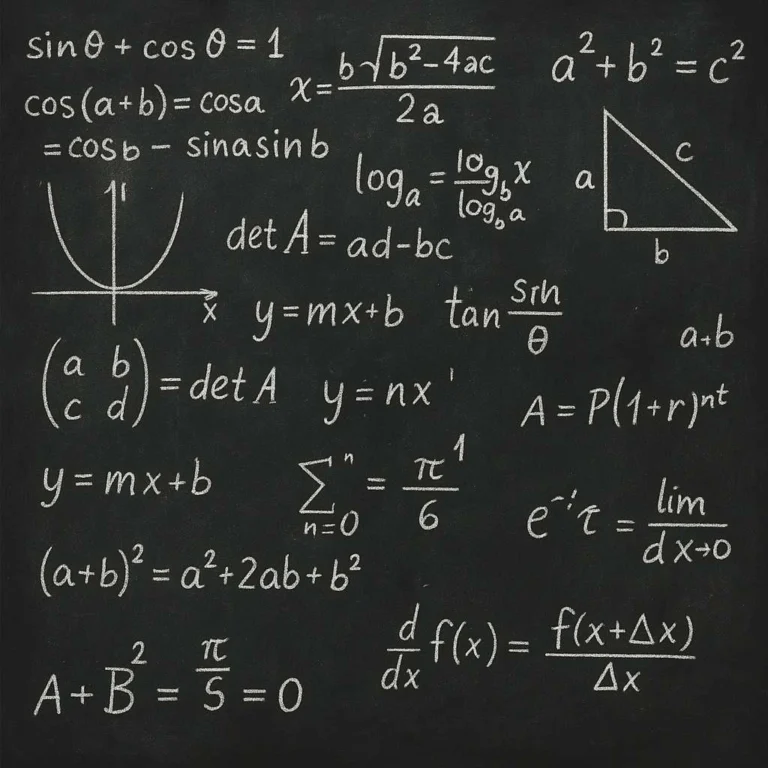
PWS is a top-tier maths coursework service with over 3,000 Ph.D. writers, guaranteeing 100% original work, free plagiarism reports, unlimited revisions, and free topic ideas. It offers academic freedom, full ownership, and user rights.

Progressive Writing Skills is a top-tier English coursework service with 1,500 native writers, 10,000 students achieving A+ grades, and offers 100% plagiarism-free work, secure payments, and unlimited revisions.

Analyze visuals, performances, and themes with examples—rewatch thoughtfully and write with purpose. This captures the core of crafting an insightful movie review: observation, analysis, and clarity.

A reaction paper analyzes and critiques a work, expressing insights, evaluating themes, and reflecting.

MACA 2013–15: 2014 saw strong revenue & profit growth; in 2015, lower asset efficiency emerged, yet liquidity & dividends remained robust.
Analyzing NatWest's use of monetary rewards to enhance employee motivation, performance, and alignment with Maslow's hierarchy of needs.

The essay explores the dangers of diet pills marketed for quick weight loss, emphasizing their misleading promises of rapid results without diet or exercise. It highlights the harmful effects of ingredients like ephedra, linked to serious health risks, and examines the role of advertising in creating unrealistic body standards, especially for women. The research underlines the importance of adopting healthy, sustainable weight loss methods such as balanced nutrition and exercise. It urges obese individuals, particularly women and teenagers, to understand the long-term risks of diet pills and focus on natural weight management approaches for overall well-being.

The impact of minimum wage increases on joblessness duration and employment is complex. While traditional neoclassical theory suggests that higher minimum wages lead to increased joblessness, alternative theories like competence pay and monopsony models indicate that higher wages may reduce joblessness periods. Increased wages can motivate workers, improve job skills, and boost employment in markets with low competition or non-competitive structures. While minimum wage hikes may not necessarily lead to longer unemployment durations, they can affect workers' decisions to participate in the labor force, potentially shortening joblessness periods in certain contexts.

Cost-Effectiveness Analysis (CEA) evaluates diverse interventions to maximize health benefits by comparing costs and outcomes, helping policymakers allocate scarce resources. Cost-Utility Analysis (CUA) assesses interventions using quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), useful when budgets are constrained. Discounting adjusts future costs and benefits to present values, reflecting society’s preference for immediate rewards. Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) compares policies or projects by quantifying their costs and benefits in monetary terms, though it's challenging for intangible programs. CEA is widely used in health policy, but its reliability depends on data quality and sensitivity analyses to address variations and uncertainties.